ESP32: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
[[category:CVE]] | [[category:CVE]] | ||
[[category:Development Boards]] | [[category:Development Boards]] | ||
[[category:Devices]] | |||
* ESP32-pi https://www.hackster.io/news/sequent-microsystems-esp32-pi-aims-to-address-raspberry-pi-supply-shortages-for-some-use-cases-2dddc70ba29a | * ESP32-pi https://www.hackster.io/news/sequent-microsystems-esp32-pi-aims-to-address-raspberry-pi-supply-shortages-for-some-use-cases-2dddc70ba29a | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 16 May 2023
comparisons
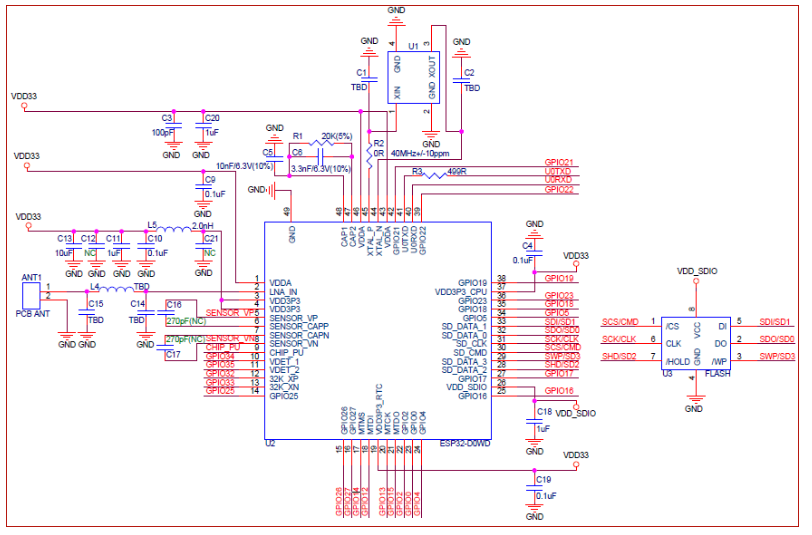
ESP32
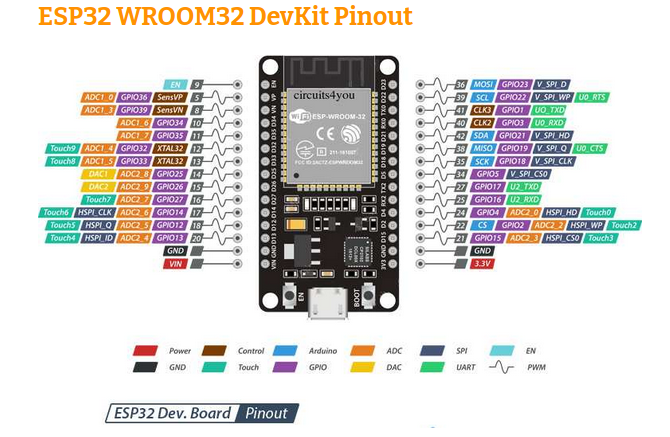
ESP32S
- https://www.espressif.com/en/support/documents/technical-documents
- https://www.amazon.com.au/ESP-WROOM-32-Development-Bluetooth-Ultra-Low-Consumption/dp/B07Z1RH9TR/ref=sr_1_7?dchild=1&keywords=esp32&qid=1630275723&s=electronics&sr=1-7
- https://www.amazon.com.au/Development-Supports-ESP32-CAM-Intelligent-Equipment/dp/B08CDCSQHL/ref=sr_1_3_sspa?dchild=1&keywords=esp32&qid=1630275723&s=electronics&sr=1-3-spons&psc=1&spLa=ZW5jcnlwdGVkUXVhbGlmaWVyPUEyTTZPWDdTVTdLV1ZDJmVuY3J5cHRlZElkPUEwMjYyNjI4NDdWQTE2QzFFWFozJmVuY3J5cHRlZEFkSWQ9QTFNSFBWREQwRDZUVDMmd2lkZ2V0TmFtZT1zcF9hdGYmYWN0aW9uPWNsaWNrUmVkaXJlY3QmZG9Ob3RMb2dDbGljaz10cnVl
- camera
- https://www.amazon.com.au/Development-Supports-ESP32-CAM-Intelligent-Equipment/dp/B08CDCSQHL/ref=sr_1_3_sspa?dchild=1&keywords=esp32&qid=1630275723&s=electronics&sr=1-3-spons&psc=1&spLa=ZW5jcnlwdGVkUXVhbGlmaWVyPUEyTTZPWDdTVTdLV1ZDJmVuY3J5cHRlZElkPUEwMjYyNjI4NDdWQTE2QzFFWFozJmVuY3J5cHRlZEFkSWQ9QTFNSFBWREQwRDZUVDMmd2lkZ2V0TmFtZT1zcF9hdGYmYWN0aW9uPWNsaWNrUmVkaXJlY3QmZG9Ob3RMb2dDbGljaz10cnVl
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MKiITEsOwRA&feature=youtu.be
- https://www.espressif.com/en/products/devkits/esp32-devkitc/overview
- https://www.amazon.com.au/NodeMcu-Wireless-Internet-Development-ESP8266/dp/B098NFQTMT/ref=sr_1_13_sspa?crid=3QSM2UM882Y21&dchild=1&keywords=esp8266+nodemcu&qid=1630274953&s=electronics&sprefix=ESP%2Celectronics%2C427&sr=1-13-spons&psc=1&spLa=ZW5jcnlwdGVkUXVhbGlmaWVyPUExVFpNMTNERlhOMjJWJmVuY3J5cHRlZElkPUEwMTM3MjE4MVpCVElXUjBKUTFaSSZlbmNyeXB0ZWRBZElkPUEzM0k0TlNBQTJYN0pOJndpZGdldE5hbWU9c3BfbXRmJmFjdGlvbj1jbGlja1JlZGlyZWN0JmRvTm90TG9nQ2xpY2s9dHJ1ZQ==
- https://www.espressif.com/en/products/socs/esp32
ESP8266 NodeMCU
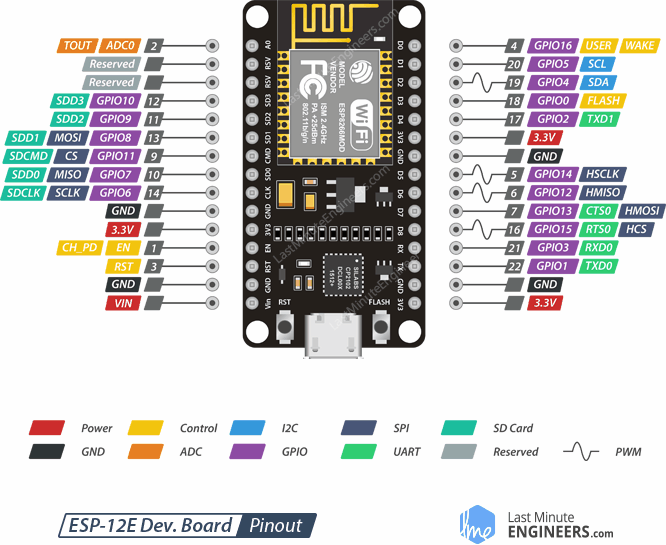 |
ESP-01
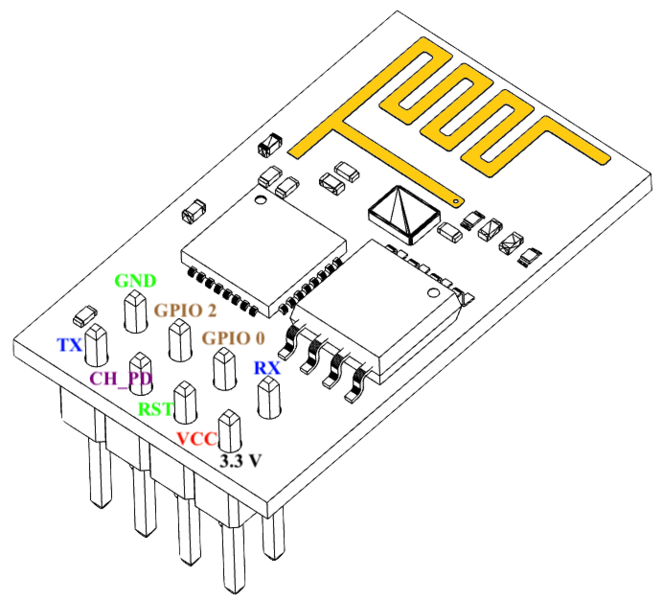 |
The pinout is as follows for the common ESP-01 module:
- GND, Ground (0 V)
- GPIO 2, General-purpose input/output No. 2
- GPIO 0, General-purpose input/output No. 0
- RX, Receive data in, also GPIO3
- VCC, Voltage (+3.3 V; can handle up to 3.6 V)
- RST, Reset
- CH_PD, Chip power-down
- TX, Transmit data out, also GPIO1
ESP-12F
 |
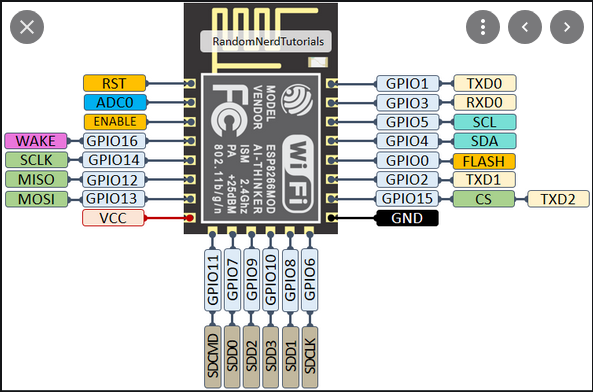 |
suppliers
ESP32S dev boards
- U$3.29 ESP32S CP2102 dev
ESP32S modules
- U$1.64 ESP32S module
ESP8266 dev boards
Development boards make it relatively easy to setup an IDE on a computer and cross-compile code to be loaded into the target module (which contains an ESP chip).
ESP8266 modules
- A$3.76 ESP8266 ESP-12F 12S
audio
- audio player https://www.instructables.com/ESP32-Audio-Player/
- hackster https://www.hackster.io/julianfschroeter/stream-your-audio-on-the-esp32-2e4661
- picoAudio https://hackaday.com/2019/10/06/professional-audio-on-an-esp32/
- audio sampling https://www.toptal.com/embedded/esp32-audio-sampling
ESP CVE
- Blue Tooth https://hackaday.com/2021/09/23/bluetooth-vulnerability-arbitrary-code-execution-on-the-esp32-among-others/?fbclid=IwAR3iELpa5ZEkpIk6BtpNNKrPcokjV-4rfprSGibgTh7PTN68kaX9MaJtKsM
- Zero PMK Installation (CVE-2019-12587)
- ESP32/ESP8266 EAP Client Crash (CVE-2019-12586)
- ESP8266 Beacon Frame Crash (CVE-2019-12588)
- CVE-2019-17391 attacks the device cryptography through voltage glitching https://www.infoq.com/news/2019/12/esp32-fatal-fury/
- https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvekey.cgi?keyword=ESP32
Development
- Using arduino IDE https://iotdesignpro.com/projects/getting-started-with-esp32-program-it-using-arduino-ide-blinking-led
- arduino IDE on a pi https://electropeak.com/learn/install-arduino-ide-on-raspberry-pi/